Information security is the practice of protecting information by mitigating information risks. It involves the protection of information systems and the information processed, stored, and transmitted by these systems from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. This includes the protection of personal information, financial information, and sensitive or confidential information stored in both digital and physical forms. Effective information security requires a comprehensive and multi-disciplinary approach, involving people, processes, and technology.
Information security (INFOSEC) builds on the CIA triad—confidentiality, integrity, and availability—to protect data across its lifecycle states: storage, processing, and transmission. Countermeasures like policies, procedures, education, and training address threats and vulnerabilities, with detailed examples enhancing practical understanding from prior basics.
Availability Expanded
Availability ensures authorized users access information promptly, countering disruptions like DDoS attacks that flood servers. In processing states, countermeasures include rate limiting and failover clustering; for instance, cloud providers like AWS use auto-scaling groups to redistribute load during traffic spikes, preventing e-commerce outages. Threats involve ransomware locking files, mitigated by regular backups tested for restoration.
Confidentiality Expanded
Confidentiality prevents unauthorized disclosure through controls like role-based access (RBAC) and encryption algorithms such as AES-256. During storage, tools like LUKS encrypt partitions on Linux systems, protecting against physical theft as in lost laptops. Transmission uses protocols like IPsec for VPNs, exemplified by remote workers securing corporate data over public networks against sniffers.
Integrity Expanded
Integrity verifies data remains unaltered using mechanisms like checksums (MD5, though SHA-256 preferred for security) and blockchain for tamper-proof logs. In storage, file integrity monitoring (FIM) tools like Tripwire alert on changes; a bank database example detects unauthorized balance edits. Processing threats, such as SQL injection, are countered by input validation and prepared statements.
Information States Detailed
Storage: Data at rest faces risks like theft; countermeasures include immutable storage and air-gapping critical backups.
Processing: Active computation vulnerable to side-channel attacks; secure multi-party computation (SMPC) enables analysis without exposure.
Transmission: In transit, risks include interception; countermeasures like zero-trust networks verify every packet.
Countermeasures Deep Dive
Education/Training/Awareness: Phishing simulations train users; example—annual certifications reduce click rates by 40% in firms.
Policies/Procedures/Practices: Policies mandate MFA; procedures detail patch management; practices deploy SIEM for real-time monitoring.
NIST SP 800-53 outlines control families like AC (access control).
Threats and Vulnerabilities Examples
Threats: External (APT groups like SolarWinds hack), internal (disgruntled employees). Vulnerabilities: Zero-days in software, misconfigurations like open S3 buckets. Counterexample—Equifax breach from unpatched Apache Struts exposed 147M records, stressing patching urgency.
What is Information Security (InfoSec)?
Information Security is not only about securing information from unauthorized access. Information Security is basically the practice of preventing unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, inspection, recording, or destruction of information. Information can be a physical or electronic one. Information can be anything like Your details or we can say your profile on social media, your data on your mobile phone, your biometrics, etc. Thus Information Security spans so many research areas like Cryptography, Mobile Computing, Cyber Forensics, Online Social Media, etc.
During the First World War, a Multi-tier Classification System was developed keeping in mind the sensitivity of the information. With the beginning of the Second World War, formal alignment of the Classification System was done. Alan Turing was the one who successfully decrypted the Enigma Machine which was used by Germans to encrypt warfare data.
Effective information security requires a comprehensive approach that considers all aspects of the information environment, including technology, policies and procedures, and people. It also requires ongoing monitoring, assessment, and adaptation to address emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
Why We Use Information Security?
We use information security to protect valuable information assets from a wide range of threats, including theft, espionage, and cybercrime. Here are some key reasons why information security is important:
- Protecting sensitive information: Information security helps protect sensitive information from being accessed, disclosed, or modified by unauthorized individuals. This includes personal information, financial data, and trade secrets, as well as confidential government and military information.
- Mitigating risk: By implementing information security measures, organizations can mitigate the risks associated with cyber threats and other security incidents. This includes minimizing the risk of data breaches, denial-of-service attacks, and other malicious activities.
- Compliance with regulations: Many industries and jurisdictions have specific regulations governing the protection of sensitive information. Information security measures help ensure compliance with these regulations, reducing the risk of fines and legal liability.
- Protecting reputation: Security breaches can damage an organization's reputation and lead to lost business. Effective information security can help protect an organization's reputation by minimizing the risk of security incidents.
- Ensuring business continuity: Information security helps ensure that critical business functions can continue even in the event of a security incident. This includes maintaining access to key systems and data, and minimizing the impact of any disruptions.
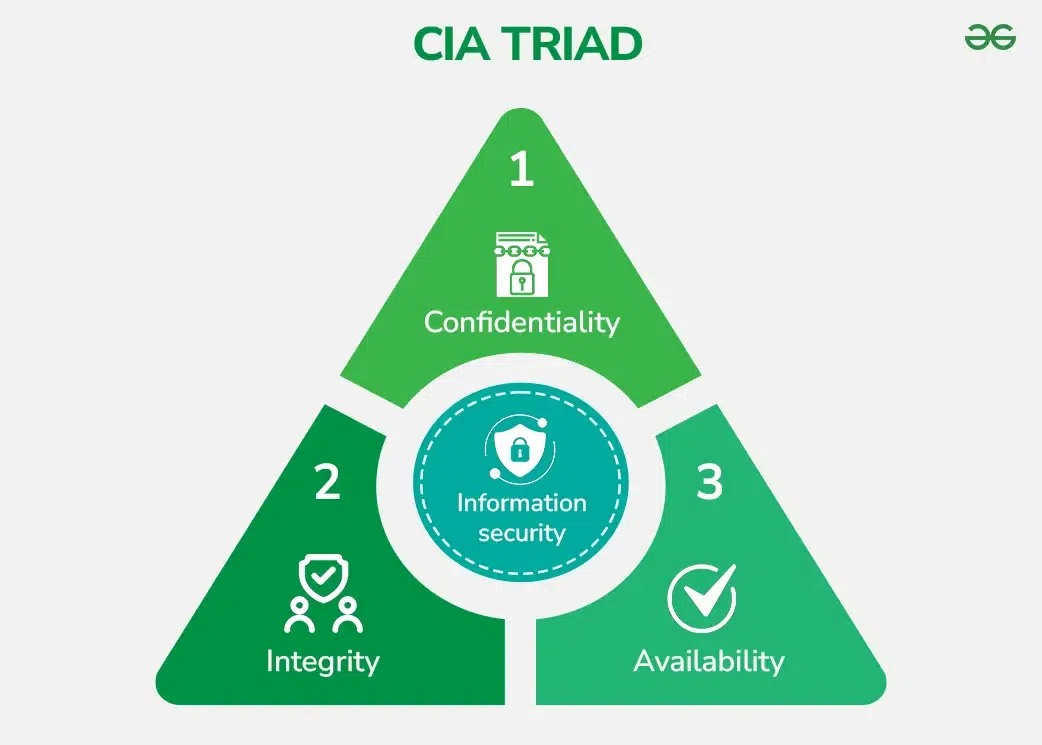
What are the 3 Principles of Information Security?
Information security is necessary to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information, whether it is stored digitally or in other forms such as paper documents. Information Security programs are build around 3 objectives, commonly known as CIA - Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability.
- Confidentiality - Means information is not disclosed to unauthorized individuals, entities and process. For example if we say I have a password for my Gmail account but someone saw while I was doing a login into Gmail account. In that case my password has been compromised and Confidentiality has been breached.
- Integrity - Means maintaining accuracy and completeness of data. This means data cannot be edited in an unauthorized way. For example if an employee leaves an organisation then in that case data for that employee in all departments like accounts, should be updated to reflect status to JOB LEFT so that data is complete and accurate and in addition to this only authorized person should be allowed to edit employee data.
- Availability - Means information must be available when needed. For example if one needs to access information of a particular employee to check whether employee has outstanded the number of leaves, in that case it requires collaboration from different organizational teams like network operations, development operations, incident response and policy/change management. Denial of service attack is one of the factor that can hamper the availability of information.
Apart from this there is one more principle that governs information security programs. This is Non repudiation.
- Non repudiation - Means one party cannot deny receiving a message or a transaction nor can the other party deny sending a message or a transaction. For example in cryptography it is sufficient to show that message matches the digital signature signed with sender's private key and that sender could have a sent a message and nobody else could have altered it in transit. Data Integrity and Authenticity are pre-requisites for Non repudiation.
- Authenticity - Means verifying that users are who they say they are and that each input arriving at destination is from a trusted source.This principle if followed guarantees the valid and genuine message received from a trusted source through a valid transmission.
- Accountability - This means that it should be possible to trace actions of an entity uniquely to that entity. For example as we discussed in Integrity section Not every employee should be allowed to do changes in other employees data. For this there is a separate department in an organization that is responsible for making such changes and when they receive request for a change then that letter must be signed by higher authority.
What is an Information Security Management System (ISMS)?
An Information Security Management System (ISMS) is a structured framework designed to protect an organization's information assets. It includes policies, procedures, and controls to manage and secure sensitive data from threats like unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyberattacks. By following international standards like ISO/IEC 27001, an ISMS helps organizations identify risks, implement security measures, and continuously improve their security practices to safeguard their information.
What is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)?
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a comprehensive privacy law established by the European Union (EU) to protect individuals' personal data. Effective since May 25, 2018, GDPR sets strict rules on how personal data is collected, used, stored, and shared. It grants individuals more control over their data, including rights to access, correct, and delete their information. GDPR also requires organizations to be transparent about their data practices and to implement strong security measures. Non-compliance can result in significant fines, emphasizing the importance of safeguarding personal data and respecting privacy rights.
Types of Information Security
Information Security (InfoSec) focuses on protecting data from threats and unauthorized access. Here are five important types:
- Network Security: Protects computer networks from attacks and unauthorized access using tools like firewalls, Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), and Virtual Private Networks (VPNs). For example, a firewall can block malicious traffic trying to enter a company's network.
- Application Security: Secures software applications by finding and fixing vulnerabilities, using methods like code reviews and security patches. An example is a web application firewall (WAF) that prevents attacks on websites by filtering and monitoring HTTP traffic.
- Data Security: Ensures data safety during storage and transfer by using encryption and data masking. For instance, encrypted emails are unreadable to anyone without the decryption key, protecting sensitive information.
- Endpoint Security: Secures individual devices such as computers, smartphones, and tablets through antivirus software and Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) tools. An example is an antivirus program that scans and removes malware from a personal laptop.
- Cloud Security: Protects data and applications hosted in cloud environments with measures like secure cloud configurations and Identity and Access Management (IAM). For instance, using multi-factor authentication (MFA) helps ensure that only authorized users can access cloud-based services.
Why is Information Security Important?
Advantages for implementing an information classification system in an organization's information security program:
- Improved security: By identifying and classifying sensitive information, organizations can better protect their most critical assets from unauthorized access or disclosure.
- Compliance: Many regulatory and industry standards, such as HIPAA and PCI-DSS, require organizations to implement information classification and data protection measures.
- Improved efficiency: By clearly identifying and labeling information, employees can quickly and easily determine the appropriate handling and access requirements for different types of data.
- Better risk management: By understanding the potential impact of a data breach or unauthorized disclosure, organizations can prioritize resources and develop more effective incident response plans.
- Cost savings: By implementing appropriate security controls for different types of information, organizations can avoid unnecessary spending on security measures that may not be needed for less sensitive data.
- Improved incident response: By having a clear understanding of the criticality of specific data, organizations can respond to security incidents in a more effective and efficient manner.
There are some potential disadvantages for implementing an information classification system in an organization's information security program:
- Complexity: Developing and maintaining an information classification system can be complex and time-consuming, especially for large organizations with a diverse range of data types.
- Cost: Implementing and maintaining an information classification system can be costly, especially if it requires new hardware or software.
- Resistance to change: Some employees may resist the implementation of an information classification system, especially if it requires them to change their usual work habits.
- Inaccurate classification: Information classification is often done by human, so it is possible that some information may be misclassified, which can lead to inadequate protection or unnecessary restrictions on access.
- Lack of flexibility: Information classification systems can be rigid and inflexible, making it difficult to adapt to changing business needs or new types of data.
- False sense of security: Implementing an information classification system may give organizations a false sense of security, leading them to overlook other important security controls and best practices.
- Maintenance: Information classification should be reviewed and updated frequently, if not it can become outdated and ineffective.
Uses of Information Security
Information security has many uses, including:
- Confidentiality: Keeping sensitive information confidential and protected from unauthorized access.
- Integrity: Maintaining the accuracy and consistency of data, even in the presence of malicious attacks.
- Availability: Ensuring that authorized users have access to the information they need, when they need it.
- Compliance: Meeting regulatory and legal requirements, such as those related to data privacy and protection.
- Risk management: Identifying and mitigating potential security threats to prevent harm to the organization.
- Disaster recovery: Developing and implementing a plan to quickly recover from data loss or system failures.
- Authentication: Verifying the identity of users accessing information systems.
- Encryption: Protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access by encoding it into a secure format.
- Network security: Protecting computer networks from unauthorized access, theft, and other types of attacks.
- Physical security: Protecting information systems and the information they store from theft, damage, or destruction by securing the physical facilities that house these systems.
Issues of Information Security
Information security faces many challenges and issues, including:
- Cyber threats: The increasing sophistication of cyber attacks, including malware, phishing, and ransomware, makes it difficult to protect information systems and the information they store.
- Human error: People can inadvertently put information at risk through actions such as losing laptops or smartphones, clicking on malicious links, or using weak passwords.
- Insider threats: Employees with access to sensitive information can pose a risk if they intentionally or unintentionally cause harm to the organization.
- Legacy systems: Older information systems may not have the security features of newer systems, making them more vulnerable to attack.
- Complexity: The increasing complexity of information systems and the information they store makes it difficult to secure them effectively.
- Mobile and IoT devices: The growing number of mobile devices and internet of things (IoT) devices creates new security challenges as they can be easily lost or stolen, and may have weak security controls.
- Integration with third-party systems: Integrating information systems with third-party systems can introduce new security risks, as the third-party systems may have security vulnerabilities.
- Data privacy: Protecting personal and sensitive information from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure is becoming increasingly important as data privacy regulations become more strict.
- Globalization: The increasing globalization of business makes it more difficult to secure information, as data may be stored, processed, and transmitted across multiple countries with different security requirements.
Conclusion
Protecting information is important in today's digital world. Different types of Information Security (InfoSec) helps to keep data safe in various ways. Network security defends networks from attacks, application security protects software from being hacked, and data security ensures that stored and transmitted data remains safe. Endpoint security secures devices like computers and phones, while cloud security safeguards data and applications in the cloud. These InfoSec types work together to keep our information secure and private across different systems and platforms.



No comments:
Post a Comment